前言
在实际开发中,我们经常会用到 vuex 来对数据进行管理,随着数据越来越多,我们逐渐开始使用一些语法糖来帮助我们快速开发。 即 vuex 中的 mapState、mapGetters、mapMutations、mapActions 等辅助函数是我们经常使用到的。
辅助函数的使用
在vue2中我们可以通过 options API 在 computed 中来使用 mapState,
1
| computed: mapsState(['name','age'])
|
在 vue3 中主要是使用 setup 来进行操作时,一般来使用vuex中数据是这样操作的,通过 useStore 这个钩子来得到
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import { useStore } from 'vuex'
import { computed } from 'vue'
setup() {
const store = useStore()
const name = computed(() => store.state.name)
const age = computed(() => store.state.age)
return {
name, age
}
},
|
这样的不足是如果数据多了,那么写起来就尤为麻烦,所以我们想到了辅助函数 mapState 来解决。
但是呢,vuex 官方并没有例子来说明如何在setup中去使用辅助函数 mapState。 所以我就尝试着以vue2的形式来写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| setup() {
const stateStore = mapState(['name', 'age'])
return {
...stateStore
}
},
|
但显示到浏览器的结果却发现是这样子的:

为什么会返回出函数呢?
为什么在setup中使用mapState会返回函数?
我试着去看了一下 mapState 的源码,发现是通过 this.$store 来拿到 store 的值的
然而在 setup 中是取不到 this 的
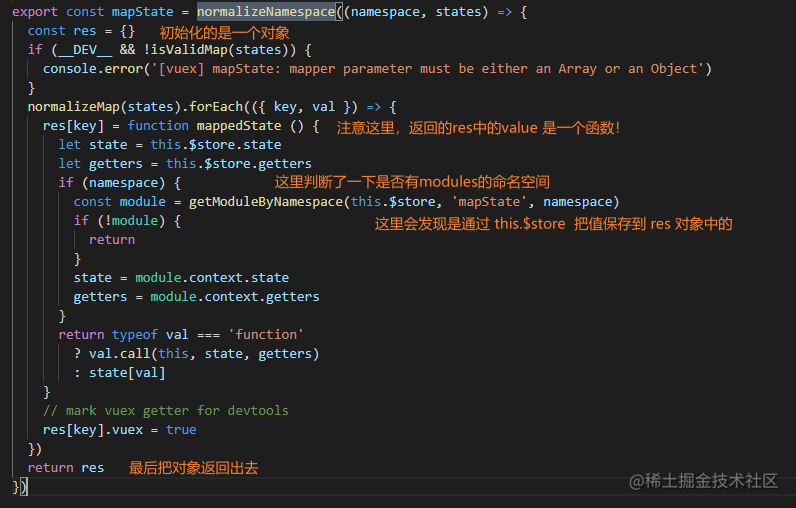
其他的辅助函数(mapGetters、mapMutations、mapActions) 同样都是这样类似的处理的。
所以通过上面的源码,我们知道:辅助函数就是会返回一个对象,而 key 是字符串, val就是函数,
类似于:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| computed:{
...mapState(['name','age'])
}
{
name: function(){},
age:function(){}
}
|
所以就明白了为什么在上述的代码中为什么会返回一个函数了。
封装一个 useState 函数
明白了其原理后,我们就知道了在 computed 中可以使用mapState, 是因为 computed 本身就是一个函数,它会接收一个函数作为参数。 我们也知道了辅助函数是 被解析成了一个对象,对象中的属性值是函数。
那么我们是不是可以试着把这俩个结合起来去封装一个hooks来使用了?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import { useStore, mapState } from 'vuex'
import { computed } from 'vue'
const useState = function(mapper) {
const store = useStore()
const storeStateFns = mapState(mapper)
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(item => {
const fn = storeStateFns[item].bind({$store, store})
storeState[item] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
export default useState
|
然后在组件中就这样使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| setup() {
const stateStore = useState(['name','age'])
return {
...stateStore
}
}
|
这样就可以在setup中使用辅助函数啦,又可以少些代码了多开心哈~
封装一个 useMapper 函数
同样的, 不止是 mapState, mapGetters 也是根据相同的思路来进行封装的,所以就稍加改造。如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { mapGetters, mapState, useStore } from 'vuex'
const useMapper = (mapper, mapFn) => {
const store = useStore()
const storeStateFns = mapFn(mapper)
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach((keyFn) => {
const fn = storeStateFns[keyFn].bind({ $store: store })
storeState[keyFn] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
export const useState = ( mapper) => {
return useMapper(mapper, mapState)
}
export const useGetters = (mapper) => {
return useMapper(mapper, mapGetters)
}
|
然后就这样的使用:
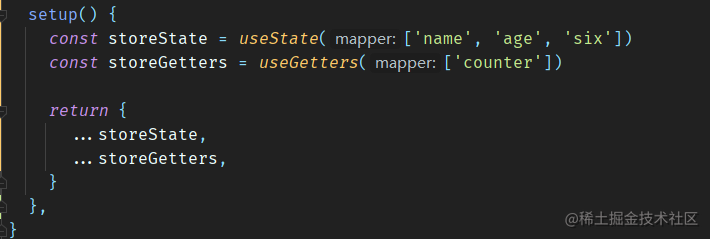
关于 mapMutations、mapActions 是不用进行封装的,原因可以自己想想
其实哈,使用mutaiton和actions中本来就是去调用方法的,所以直接就是跟辅助函数的属性值挂钩。
模块化情况下的考虑
刚刚封装的 useMapper 是没有考虑到模块化的, 在开发时,随着数据的种类越来越多,使用 modules 是不可避免的,所以我们需要对刚刚的 useMapper 进行一下 模块化边缘的处理
如下:
我们需要借助vuex提供的createNamespacedHelpers函数来得到模块中的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| import { computed } from 'vue'
import { mapGetters, mapState, useStore, createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const useMapper = (mapper, mapFn) => {
const store = useStore()
const storeStateFns = mapFn(mapper)
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach((keyFn) => {
const fn = storeStateFns[keyFn].bind({ $store: store })
storeState[keyFn] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
export const useState = (moduleName, mapper) => {
let mapperFn = mapState
if (typeof moduleName === 'string' && moduleName.length > 0) {
mapperFn = createNamespacedHelpers(moduleName).mapState
} else {
mapper = moduleName
}
return useMapper(mapper, mapperFn)
}
export const useGetters = (moduleName, mapper) => {
let mapperFn = mapGetters
if (typeof moduleName === 'string' && moduleName.length > 0) {
mapperFn = createNamespacedHelpers(moduleName).mapGetters
} else {
mapper = moduleName
}
return useMapper(mapper, mapperFn)
}
|
使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| setup(){
const storeState = useState(['name', 'age', 'six'])
const storeGetters = useGetters(['counter'])
const homeState = useState('home', ['homeCounter'])
return {
...storeState,
...storeGetters,
...homeState
}
}
|
总结
在vue2中习惯了使用辅助函数,但是在vuex文档中没有找到在vue3内如何使用辅助函数,然后一直去使用 computed 来去包裹 store 来获取值,随着数据的增多,使用起来也很麻烦,所以就封装了这样一个函数来提高开发效率。
